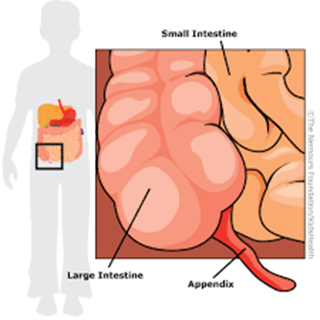
APPENDICITIS IN CHILDREN
What are the symptoms of Appendicitis?
The first signs of appendicitis are often pain around the belly button. It might seem like just a stomachache. This pain usually gets worse and moves to the lower right side of the belly.
- Low-grade fever
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea (feeling sick) and vomiting (throwing up).
- Diarrhea (especially small amounts, with mucus).
- Swollen belly
If pain spreads across the belly, it may mean the appendix has burst. It is called ruptured appendicitis.
Why is Appendicitis a concern ?
If an infected appendix isn’t removed, it has the potential to burst inside within 48 to 72 hours of the first symptoms. Left untreated, this might form a large collection of pus (an abscess) or spread throughout the belly or in severe cases, through the blood to the rest of the body.
How is the diagnosis made?
After a detailed history and clinical , examination, the pediatric surgeon would confirm the diagnosis with the following tests :
- Ultrasound of abdomen
- Blood tests : CBC
- CT scan of abdomen
How is Appendicitis treated?
Appendicitis is a surgical emergency. If left untreated, it will burst and the infection will spread and the condition of the child may get critical. Hence, emergency Appendectomy is advocated, either through routine open technique or laparoscopically (minimally invasive or Key hole Surgery)
Pain abdomen | Appendix | Appendicitis | Laparoscopic Appendectomy